One of the most useful and versatile body parts is the hand. They are constantly in use, whether you are chopping fruit, working on your automobile, or simply browsing this blog. Knowing how to prevent hand injuries is important because, if you\’ve ever had one, you know that even the smallest amount of discomfort can make it difficult to perform any activity. Here are some of the most frequent hand injuries, their effects on your life, and the best ways to prevent them.
Common Hand Injuries
Cuts
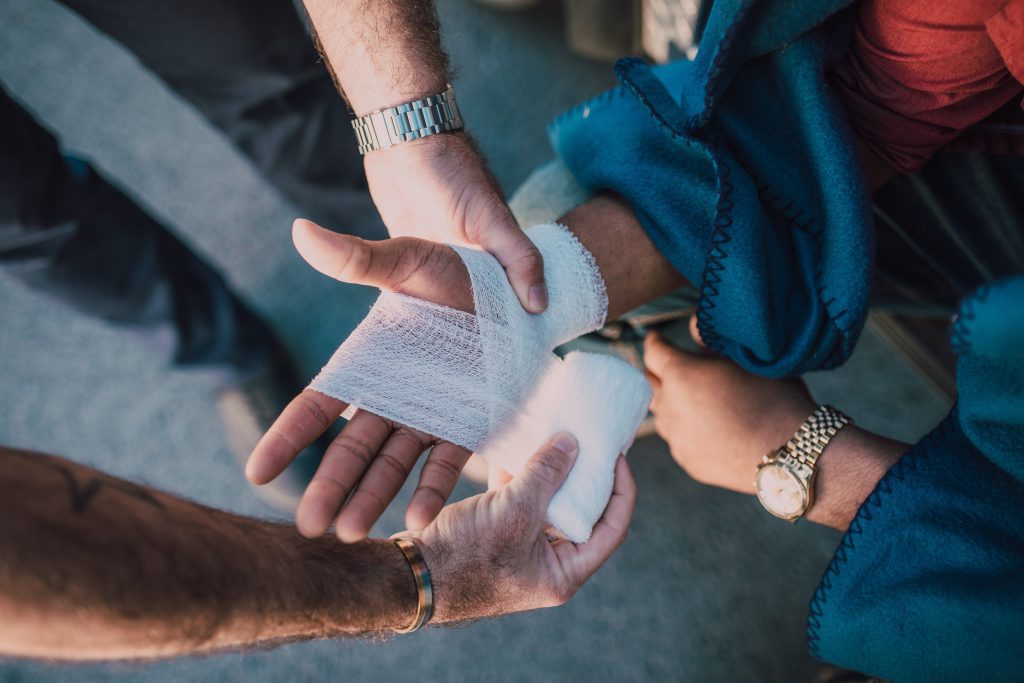
Most of us know what a cut is and how it might occur, but it is still important to go over these topics in detail. Thin paper, rough concrete surfaces, and sharp glass are just a few examples of the several things that might cause cuts. They\’re among the most frequent injuries, and they also happen to be among the simplest to avoid and treat. It\’s always ideal to avoid cuts as much as you can. Deep gashes can cause issues with bones and ligaments.
Ligaments and Tendons Injuries
Ligaments and tendons hold the parts of the hand together and aid in movement. Significant injuries to these body parts can be extremely uncomfortable when performing simple tasks with your hands. Incorrect knife use or receiving deep cuts from glass object fragments are the main causes of these wounds.
Sometimes tendon injuries are the result of ordinary wear and tear or age. An urgent diagnosis is required for injuries like torn flexor tendons, especially if you also have wounded fingers or blood vessel damage. If you think your severe cut or hand injury may have caused torn ligaments and tendons, consult a professional.
Wrist Injuries
Because the hand and wrist are interconnected, any wrist injury will also affect your range of motion and general capacity to carry out simple tasks. Using your hand to brace yourself against a fall frequently results in wrist fractures. If the bone is significantly misaligned or has several cracks, surgery is necessary. Typically, casts are applied to the wrist to prevent additional injury and promote healing. A much-weakened hand and a lifetime of stiffness can result from severe wrist injuries or insufficient recovery.
Fractures
Fractures are significantly more painful and hazardous than cuts, which puncture the skin and cause minor bleeding. Hand fractures happen when a hand bone breaks or chips, and they\’re typically brought on by using too much effort. Broken bones mend at various speeds, although most fractures can mend in 4-6 weeks. One of the most frequent hand injuries is a boxer\’s fracture, which usually affects people between the ages of 16 and 29 and is brought on by slamming against a wall or other immovable object.
Severed Fingertips
Severed fingertips are among the most frequent hand injuries for many industrial or construction workers. They can be caused by table saws, circular saws, hands caught in narrow areas or being jammed between sharp items. One of the more severe hand injuries can also be brought on by accidentally getting caught between lawnmowers or snowblower blades. Surgery and subsequent follow-up operations may be necessary during the months-long recovery process.
Tips to Prevent Common Hand Injuries
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that more than 100,000 workers in private businesses sustained hand injuries in 2020. Three high-risk workplaces accounted for 43% of all hand injuries. Manufacturing accounted for one-third of hand injuries. 3,000 workers in the mining and natural resource sectors sustained hand injuries. In addition, 2,700 hand injuries occurred in the fishing, hunting, forestry, and agriculture sectors.
When workers use hazardous tools and equipment that include pinch points, moving parts, hot and cold spots, or automation, prevention is extremely crucial.
Ensuring employees know the risks associated with their occupations and how to avoid them is the first step in safety training. The next stage for you as a manager of safety or training is to put mechanisms in place to stop these major sources of serious injury.
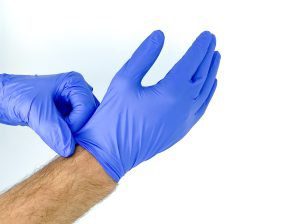
Wear the Proper Gear
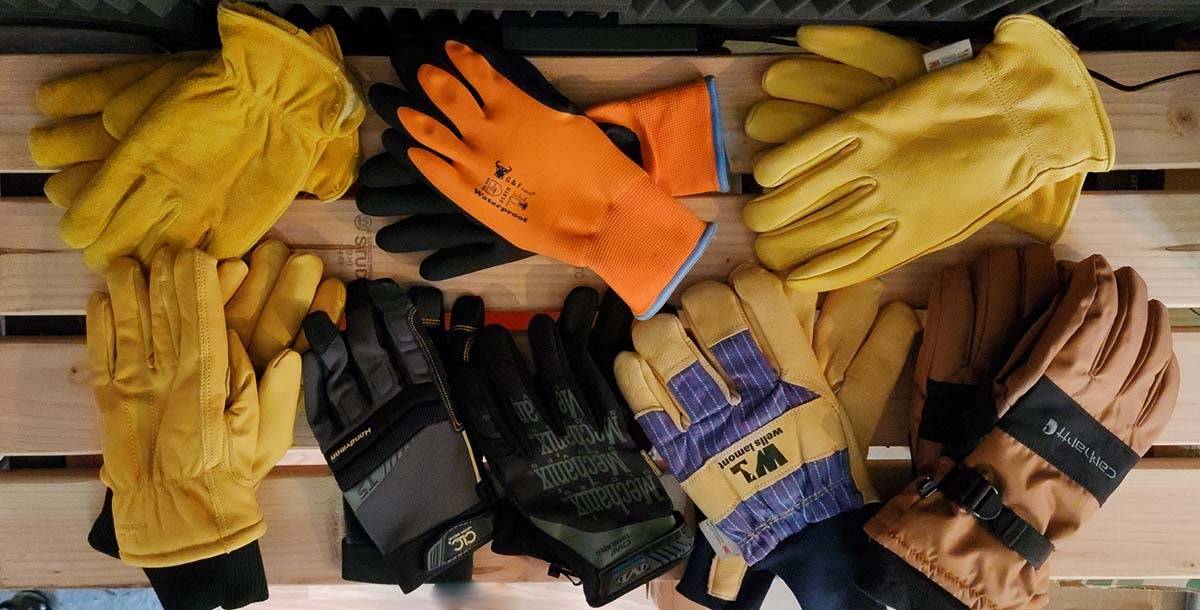
Wearing the proper work gloves is the simplest method for preventing hand injuries. The right gloves protect against heat and cold, halt splinters and slivers, prevent punctures and cuts from sharp materials, and keep germs and dangerous substances off the skin.
Wear gloves that fit properly because ill-fitting gloves risk getting entangled in equipment. Additionally, inspect the gloves for damage and put them on each time they arrive for their safety.
Inspect your Equipment
Only in good condition can your protection equipment perform as intended. Before beginning work, check your equipment for holes, tears, or a buildup of debris and other items. Replace your gloves right away if they are subpar.
Consider wearing brightly colored gloves as a constant reminder to take care of your hands, and switch up the color of the gloves frequently to keep the reminder in your head.
Perform Job Safety Analysis
Before beginning the job, complete a Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA). You can note the hazards in your workplace, such as pinch points, electrical exposure, weariness, and distraction. By painting the dangers a different color or using stickers, you can use this information to identify pinch spots on the job site.
Familiarize Machine Guards
Machine guards, which the manufacturer typically installs, operate as barriers between you and a machine\’s potentially harmful components. However, a machine guard is only effective when you use it correctly. Follow the manufacturer\’s instructions carefully, and do not remove the guard without permission.
Final Thoughts: Prevent Hand Injuries with an Effective Safety Program
Three methods of preventing hand injuries at work are included in best practices for an occupational safety program: Engineering Controls, Administrative Controls, and PPE.
Engineering Controls
Engineering controls use machinery with built-in safety mechanisms to decrease risks. Safety guards, electrical proximity limiting devices, emergency stop devices, and ergonomic tools are common engineering controls.
Administrative Controls
When you cannot implement engineering controls or effectively decrease the risk surrounding a particular hazard, management will put administrative controls in place. Administrative measures comprise safety education, physical safety barriers such as lockout tagout devices, warning signs, product replacements, and ergonomic considerations.
PPE, or Personal Protective Equipment
Companies must provide PPE, typically work gloves, to protect employees at risk of hand injuries when engineering and administrative controls are not practical or sufficient.